The COVID-19 pandemic has presented numerous challenges to global health, not the least of which is the emergence of various SARS-CoV-2 variants. These variants, which arise due to mutations in the virus’s genetic material, have the potential to affect transmissibility, severity of illness, and vaccine efficacy. This article delves into what COVID-19 variants are, how they have evolved, their implications for public health, and what individuals can do to protect themselves and others.
What Are COVID-19 Variants?
COVID-19 variants are versions of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that have undergone mutations. While mutations occur naturally as viruses replicate, some variants may have characteristics that differ significantly from the original virus. Variants can be classified based on their impact on public health:
- Variants of Interest (VOIs): These variants have genetic changes that are predicted or known to affect virus characteristics, such as transmissibility or disease severity.
- Variants of Concern (VOCs): These variants have been shown to cause increased transmissibility, more severe disease, reduced effectiveness of treatments or vaccines, or diagnostic detection failures.
- Variants of High Consequence: Currently, no variants have been classified as high consequence, as none are known to significantly diminish the effectiveness of preventive measures.
The Evolution of Variants

Since the onset of the pandemic, several significant variants have emerged. Some of the most notable variants include:
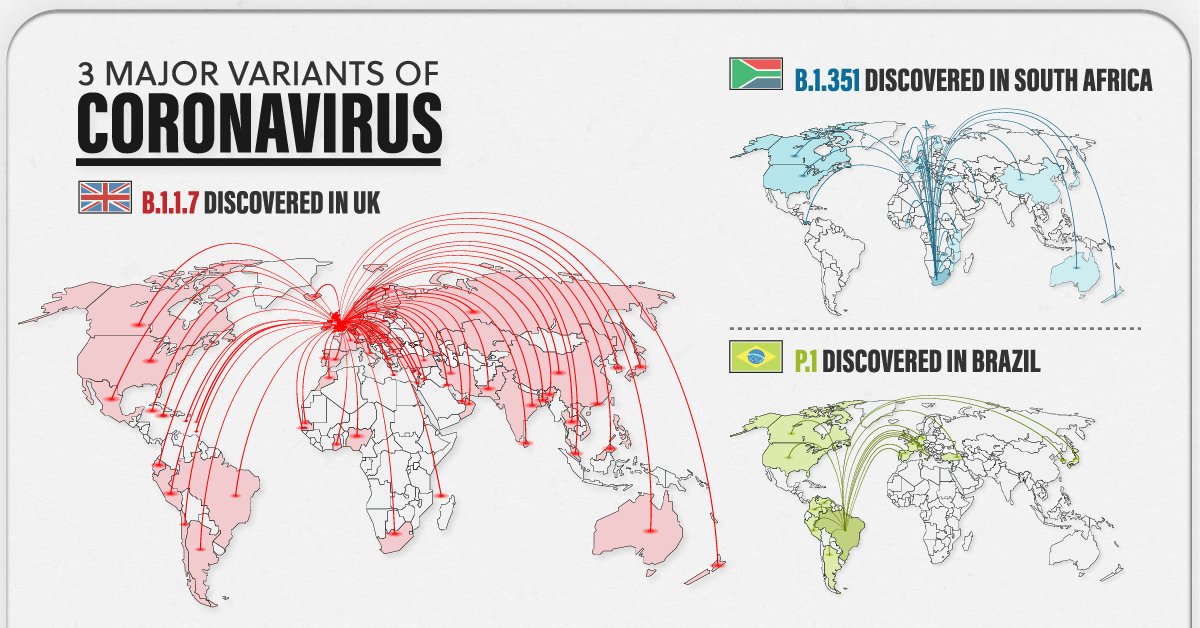
- Alpha (B.1.1.7): First identified in the UK, this variant was associated with increased transmissibility and was considered a VOC in late 2020.
- Beta (B.1.351): Detected in South Africa, this variant showed resistance to certain monoclonal antibody treatments and reduced vaccine effectiveness.
- Gamma (P.1): Originating in Brazil, this variant also demonstrated resistance to some vaccine-induced immunity.
- Delta (B.1.617.2): First identified in India, the Delta variant became the dominant strain in many countries due to its high transmissibility.
- Omicron (B.1.1.529): Detected in late 2021, Omicron has numerous mutations and raised concerns about vaccine effectiveness, though it generally causes milder illness.
Public Health Implications
The emergence of COVID-19 variants poses several public health challenges:
- Increased Transmissibility: Variants like Delta have demonstrated higher transmission rates, leading to surges in cases even in populations with high vaccination rates.
- Impact on Vaccine Efficacy: Some variants show reduced susceptibility to vaccines, although vaccines continue to provide significant protection against severe disease.
- Effects on Treatments: Certain monoclonal antibody treatments have been less effective against some variants, necessitating ongoing research and adaptation.
- Need for Continued Surveillance: Ongoing genomic surveillance is crucial to identify and monitor variants as they emerge and evolve.
Case Studies: Variants in Action
To illustrate the real-world impact of COVID-19 variants, consider the following case studies:
Delta Variant Surge
In mid-2021, the Delta variant led to a significant surge in COVID-19 cases across the globe. Countries like India experienced devastating waves of infections, resulting in overwhelmed healthcare systems. In the United States, the Delta variant accounted for a substantial majority of cases, prompting renewed public health measures, including mask mandates and vaccination drives. The Delta surge highlighted the importance of vaccination and public health interventions in controlling variant spread.
Omicron’s Rapid Spread

The Omicron variant, first reported in South Africa, quickly became the dominant strain in many countries due to its high transmissibility. Despite initial concerns about vaccine effectiveness, data showed that booster doses substantially increased protection against severe disease caused by Omicron. This case underscored the importance of booster vaccinations in adapting to emerging variants.
What You Can Do to Protect Yourself
As variants continue to circulate, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities:
- Get Vaccinated: Vaccination remains one of the most effective ways to protect against severe illness. Stay informed about booster recommendations.
- Practice Preventive Measures: Continue wearing masks in crowded or indoor settings, practice social distancing, and maintain good hand hygiene.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with credible sources regarding variant developments and public health recommendations.
- Get Tested: If experiencing symptoms or after potential exposure, get tested to prevent further spread of the virus.
The emergence of COVID-19 variants has underscored the dynamic nature of the virus and the ongoing challenges faced by public health systems worldwide. Understanding the characteristics and implications of these variants is crucial for effective response strategies. As we navigate this evolving landscape, vaccination remains vital, along with continued public health measures and individual vigilance. By staying informed and proactive, we can collectively mitigate the impact of COVID-19 variants and move towards a safer future.




